HuggingGPT: Giving ChatGPT Models the Ability to Use External Tools

In Brief
HuggingFace Hub is a platform that allows researchers and developers to share and collaborate on natural language processing models, datasets, and other resources.
It also provides an easy-to-use interface for finding and downloading pre-trained models for various NLP tasks.
This approach allows for greater flexibility and efficiency in the use of GPT-based language models, as they can access a wide range of specialized models without needing to be trained on each individual task.
You probably suspected that models have their own hub, a place where people upload trained models, and others can download and use them from there. Now, the industry standard for open-source models is HuggingFace Hub.

HuggingFace Hub is a platform that allows researchers and developers to share and collaborate on natural language processing models, datasets, and other resources. It also provides an easy-to-use interface for finding and downloading pre-trained models for various NLP tasks.
This article suggests allowing ChatGPT to access existing models (there are thousands of them, and they solve hundreds of different problems) through HuggingGPT. This would make training ChatGPT much easier: Rather than teaching it to draw images or translate text into speech, we could give it the opportunity to use external tools. This approach allows for greater flexibility and efficiency in the use of GPT-based language models, as they can access a wide range of specialized models without receiving any prior training. Additionally, it opens up new possibilities for developing more advanced and complex AI applications.
In total, we get something like this:
- ChatGPT receives a command in human language.
- ChatGPT translates the command into a set of “tasks” to be performed.
- For each task, among the thousands of available models, the one required is selected (according to the provided description).
- ChatGPT reads the description of the arguments to be given to the model and prepares them.
- After completing the task, ChatGPT looks at the result and moves on according to the plan, repeating steps 3–5.
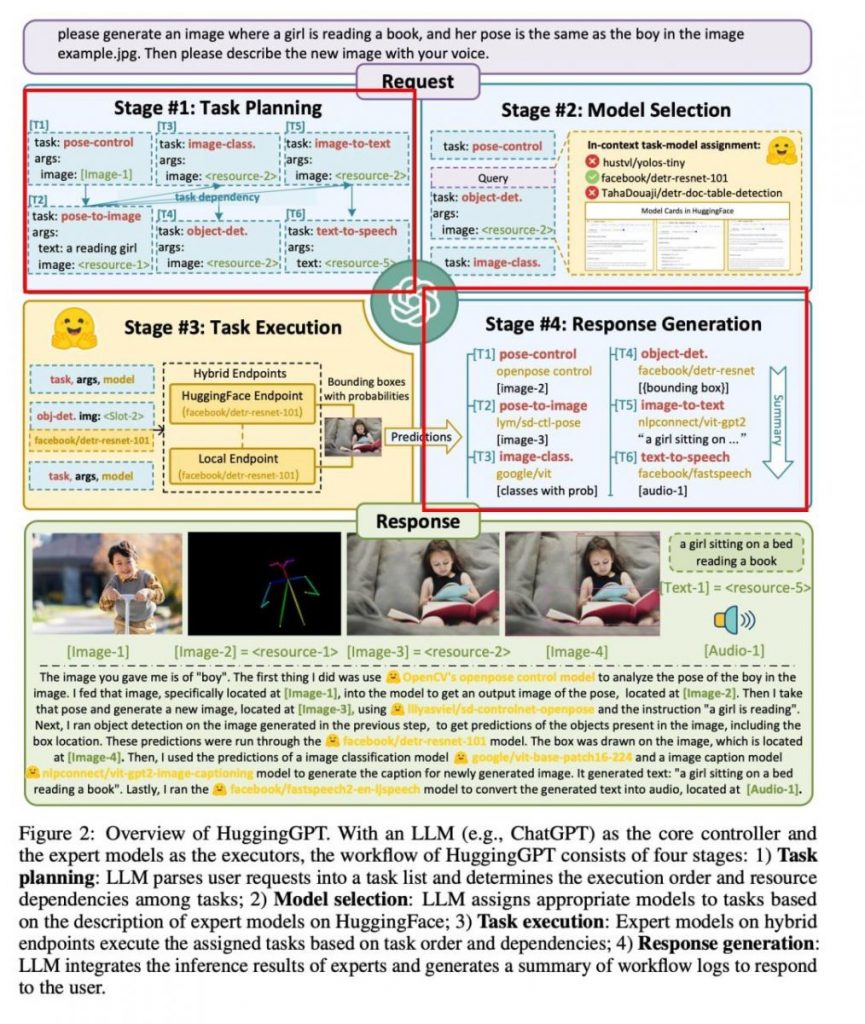
For a better understanding, consider the screenshot from the article with the following request: “Create an image of a girl reading a book, and her pose is the same as the boy’s in the image. And then describe the new image in your voice.” The model identifies as many as six tasks and successfully copes with their sequential execution.
The code is available in a repository with the very interesting name “JARVIS,” most likely a reference to the AI assistant from the movie “Iron Man.”
Read more related articles:
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, please note that the information provided on this page is not intended to be and should not be interpreted as legal, tax, investment, financial, or any other form of advice. It is important to only invest what you can afford to lose and to seek independent financial advice if you have any doubts. For further information, we suggest referring to the terms and conditions as well as the help and support pages provided by the issuer or advertiser. MetaversePost is committed to accurate, unbiased reporting, but market conditions are subject to change without notice.
About The Author
Damir is the team leader, product manager, and editor at Metaverse Post, covering topics such as AI/ML, AGI, LLMs, Metaverse, and Web3-related fields. His articles attract a massive audience of over a million users every month. He appears to be an expert with 10 years of experience in SEO and digital marketing. Damir has been mentioned in Mashable, Wired, Cointelegraph, The New Yorker, Inside.com, Entrepreneur, BeInCrypto, and other publications. He travels between the UAE, Turkey, Russia, and the CIS as a digital nomad. Damir earned a bachelor's degree in physics, which he believes has given him the critical thinking skills needed to be successful in the ever-changing landscape of the internet.
More articles

Damir is the team leader, product manager, and editor at Metaverse Post, covering topics such as AI/ML, AGI, LLMs, Metaverse, and Web3-related fields. His articles attract a massive audience of over a million users every month. He appears to be an expert with 10 years of experience in SEO and digital marketing. Damir has been mentioned in Mashable, Wired, Cointelegraph, The New Yorker, Inside.com, Entrepreneur, BeInCrypto, and other publications. He travels between the UAE, Turkey, Russia, and the CIS as a digital nomad. Damir earned a bachelor's degree in physics, which he believes has given him the critical thinking skills needed to be successful in the ever-changing landscape of the internet.



















































