Best 10 Dark Web Browsers for Anonymous Deep Web Surfing


In Brief
In this guide, we delve into the top 10 darknet browsers of 2023, evaluating their privacy, security, and user-friendliness.
Internet users can surf the dark web anonymously thanks to specialized darknet browsers. The dark web supports anonymity and free speech, but it also hosts illegal and immoral content.
| Pro Tips |
|---|
| 1. Discover the Top 15 Free Password Manager Apps of 2023 |
| 2. Explore the Top 10 VPNs Tailored for Crypto Holders in 2023, Ensuring Uncompromised Security. |
This article aims to give a thorough analysis of the top ten darknet browsers for 2023, rating them according to privacy, security, and usability standards. We’ll go into great detail about the benefits and drawbacks of each browser, supported by a useful comparison table.

Unveiling the Enigma: The Dark Web and Darknet
The phrase “dark web” refers to a region of websites and content found on overlay networks known as darknets, to which access requires particular software, setups, or authorization. Through the use of onion routing and many layers of encryption to conceal users’ names and locations, darknets provide secret and anonymous communication.
Key Illuminations about the dark web
- Accessible solely through darknet browsers like Tor or I2P, employing distinctive routing protocols.
- Recognized as a hub for unlawful pursuits such as illicit drug markets and cyber intrusions.
- Also houses legitimate endeavors such as whistleblowing and expressions of dissent in oppressive regimes.
- Facilitates concealed discourse, thereby safeguarding privacy, yet simultaneously harboring potential for illicit activities.
However, it is imperative to acknowledge that the dark web is also a realm where some users engage for illegitimate or unscrupulous purposes:
- Cybercrime Markets: Darknet markets facilitate the illicit trade of narcotics, weaponry, and contraband.
- Hacking and Malware: Darknets disseminate tools for hacking, malware, and the purloined data or credentials.
- Financial Malfeasance: The dark web becomes a hub for identity theft, tax evasion, and money laundering.
- Terrorism: Encrypted channels within the dark web can facilitate terrorist activities.
Here, we provide the top ten darknet browsers of 2023, which have been carefully compared to industry standards for privacy, security, and usability.
1. Tor Browser
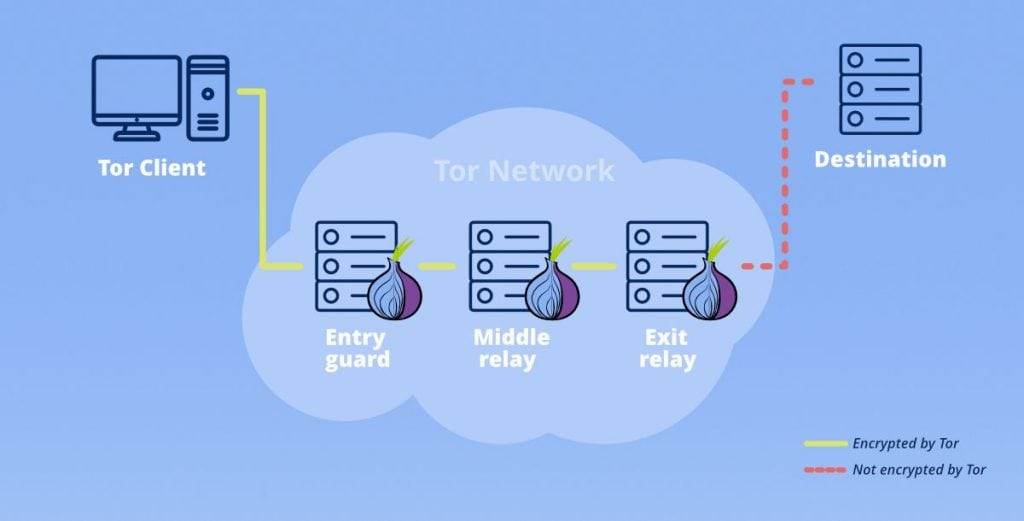
The Tor browser stands as the venerable luminary of darknet browsers, leveraging onion routing and encryption for unparalleled anonymity. Developed under the aegis of the non-profit Tor project, with sponsorship from the U.S. government and various organizations.
Privacy: Tor veils user IP addresses and locations by channeling traffic through a worldwide network of encrypted tunnels overseen by a legion of volunteer nodes. This yields an exalted level of anonymity, rendering user activities nearly untraceable.
Security: The presence of encrypted tunnels and continuous IP rotation bolsters defenses against surveillance and tracking. Traffic undergoes multiple layers of encryption, thwarting interception and monitoring attempts. The network exhibits resilience even in the face of node compromise.
User Experience: The process of downloading and configuring Tor is relatively straightforward. Its user interface, resembling Firefox ESR, provides a familiar gateway to dark web sites utilizing the .onion domain. A thriving user community augments the availability of comprehensive documentation and support.
Key Features:
- Onion routing conceals IP and location.
- Zero logging of network activity.
- Access to .onion-ending dark web sites.
- Integrated bridge relays in censored regions.
- In-built VPN and fingerprinting protection.
Limitations:
- Browsing speed may suffer due to routing encryption.
- Potential exposure to unencrypted data via malicious exit nodes.
- Some mainstream websites endeavor to block Tor access.
2. I2P
I2P, also known as the Invisible Internet Project, stands as a formidable darknet browser akin to Tor. It employs garlic routing and encryption, with dark web sites denoted by the .i2p suffix.
Privacy: I2P shepherds traffic through a decentralized peer-to-peer network, fortified with layered encryption, confounding efforts to trace activities. Every facet of I2P’s operation is shrouded in end-to-end encryption, even network database inquiries.
Security: I2P channels employ end-to-end encryption for all traffic. The network database is dispersed across nodes and shielded with encryption. Imperviousness to adversarial forces is a paramount objective.
User Experience: Setting up I2P proves to be more intricate compared to Tor, and its user interface, while functional, lacks the user-friendly polish of Tor. Documentation leans towards the technical.
Key Features:
- Garlic routing mechanism for anonymity.
- Entirely decentralized peer-to-peer network architecture.
- Concealed .i2p websites and services.
- Pervasive end-to-end encrypted tunnels.
Limitations:
- In various scenarios, I2P exhibits slower performance compared to Tor.
- The global peer network of I2P pales in comparison to Tor.
- A steeper learning curve accompanies I2P usage.
3. Brave Browser
Brave, an open-source Chromium-based web browser, places a pronounced emphasis on privacy. It incorporates an optional integrated Tor tab for clandestine browsing sessions.
Privacy: By default, Brave staunchly blocks trackers and advertisements during conventional browsing. The Tor tab funnels traffic through the Tor network, heightening anonymity during sensitive browsing sessions.
Security: Brave boasts robust security features, such as universal HTTPS enforcement. The integration of Tor introduces an additional layer of encryption when activated.
User Experience: Sporting a user-friendly interface reminiscent of Chrome, Brave makes enabling the Tor private tab via settings for expedited anonymous browsing effortless.
Key Features:
- Tor Private Tabs seamlessly integrate Tor routing.
- Default blocking of trackers and advertisements.
- Inclusion of HTTPS Everywhere encryption extension.
- Optional Brave Rewards system for contributing to websites.
Limitations:
- Advanced configuration options for Tor are absent.
- Limited isolation between Tor and non-Tor browsing.
- Shares the same browser profile, posing potential privacy risks.
4. Opera Browser
Opera, a widely embraced, multi-platform web browser, encompasses a built-in VPN service. It extends partial capabilities for dark web access via its VPN.
Privacy: The native Opera VPN conceals your IP address by funneling traffic through remote servers, amplifying anonymity. Users possess the liberty to select VPN server locations, further obfuscating their online presence.
Security: VPN encryption safeguards traffic against surveillance and monitoring. No records of activity or connections are maintained.
User Experience: Activating the built-in VPN is a breeze, requiring a simple click. Nonetheless, the options for configuring VPN servers are somewhat limited.
Key Features:
- An incorporated, boundless VPN service.
- Access to over 2,000 VPN server locations worldwide.
- Employment of robust 256-bit AES encryption.
- Absence of activity or traffic logging.
Limitations:
- VPN security may be considered inferior to Tor’s encryption.
- Opera’s VPN network encompasses fewer servers than paid services.
- Ownership of remote servers pertains to the VPN company.
5. Epic Browser
Epic Browser, staunchly committed to privacy, integrates built-in proxy support. It facilitates access to select dark web content through global proxy servers.
Privacy: Epic can channel traffic through proxy servers dispersed across diverse continents, concealing the user’s IP address. While this furnishes a modicum of anonymity, it falls short of Tor or VPN standards.
Security: Encryption stands as the bulwark between the browser and proxy servers, fortifying traffic against surveillance and data collection.
User Experience: Activating proxy support and selecting server locations proves to be remarkably straightforward, with a clean and user-friendly interface.
Key Features:
- Seamless integration of proxy servers.
- Effortless proxy activation with a single click.
- Empowerment to choose proxy server locations.
- Effective blockade of trackers and advertisements.
- Absence of user activity logging.
Limitations:
- Proxy server options are exceedingly limited.
- Proxies are less secure than Tor or VPNs.
- Lack of .onion routing capabilities.
6. GNU IceCat
GNU IceCat stands as a modified Firefox browser dedicated to privacy and freedom, birthed from the GNU open-source project.
Privacy: IceCat excels in disabling analytics services and telemetry that transmit data to Mozilla. These modifications elevate privacy standards beyond those offered by standard Firefox.
Security: IceCat builds upon Firefox’s robust security architecture, potentially incorporating extensions such as Tor for encryption.
User Experience: Boasting an interface nearly indistinguishable from Firefox, IceCat provides a sense of familiarity. However, the setup of privacy extensions necessitates a degree of effort.
Key Features:
- Disabling of analytics and tracking services.
- Transparent, open-source code.
- Compatibility with major add-ons like Tor and VPN.
- Liberation from copyright constraints and DRM.
Limitations:
- Manual setup is mandatory for VPN and Tor extensions.
- Lacks built-in dark web routing capabilities.
- Enjoys lesser recognition and a smaller community compared to Tor.
7. Comodo Dragon
Comodo Dragon, grounded in Chromium, is a browser dedicated to security and privacy. It incorporates capabilities for dark web access through extensions.
Privacy: It excels in blocking advertisements, trackers, and malicious websites. Privacy settings permit the disabling of data sharing.
Security: Comodo Dragon adopts container isolation to mitigate damage in the event of malware exposure. The browser also boasts robust antivirus capabilities.
User Experience: Familiarity abounds in the Chrome-like interface. However, dark web access mandates the installation of extensions such as Tor.
Key Features:
- Effectual blocking of advertisements, trackers, and malicious websites.
- Containers that isolate and mitigate the impact of malware.
- Privacy settings that stymie data collection.
- Compatibility with VPN and Tor extensions.
Limitations:
- Relying on add-ons for dark web access.
- The browser’s closed-source nature limits transparency.
- Ownership ties to an advertising company.
8. SRWare Iron
SRWare Iron, another Chromium-based browser ardently focused on privacy, eliminates Google tracking services and UI modifications.
Privacy: It eradicates Google services such as Google Analytics, crash reporting, and spell-checking. Data transmission to Google is tightly curtailed, imbuing a sense of transparency.
Security: While retaining the core security model of Chromium, SRWare Iron incorporates ad and script blockers for heightened security.
User Experience: The interface, nearly identical to Chrome, grants users a sense of familiarity. However, the journey to dark web access necessitates the installation of extensions.
Key Features:
- Removal of Google services and modifications.
- Options for blocking scripts and advertisements.
- Abundant advanced privacy configuration choices.
- Compatibility with Tor and VPN extensions.
Limitations:
- Dependency on plugins for dark web access.
- A less celebrated browser with a smaller user community.
- Continues to lean on the Chromium engine.
9. Waterfox

Waterfox, an open-source browser built on the foundations of Firefox, prioritizes privacy. It excises Mozilla’s analytics services.
Privacy: Waterfox disables telemetry, analytics, and Windows data collection services, significantly diminishing data sent to Mozilla.
Security: Leveraging Firefox’s existing security framework, Waterfox can incorporate extensions for encryption.
User Experience: The interface mirrors Firefox closely. However, configuring VPN or Tor necessitates a degree of manual setup.
Key Features:
- Elimination of analytics and tracking services.
- Enhanced performance optimization.
- An established codebase rooted in Firefox.
- Compatibility with major privacy extensions.
Limitations:
- Manual setup is mandatory for dark web access.
- A smaller community compared to Firefox and Tor.
- Not exclusively designed for dark web usage.
10. Darknet Proxy
Darknet Proxy, an uncomplicated Tor proxy site, offers access to the dark web without requiring installation.
Privacy: It cloaks your IP address by directing traffic through the Tor network, furnishing a modicum of anonymity. However, client encryption is conspicuously absent.
Security: The service relies entirely on Tor network encryption and lacks client-side encryption and isolation.
User Experience: No installation is required; simply load the page and commence browsing. However, customization options remain limited.
Key Features:
- A straightforward web-based Tor proxy.
- Zero installation prerequisites.
- Swift access to dark websites.
- A smattering of customization choices.
Limitations:
- The feature set is exceedingly sparse compared to the comprehensive Tor Browser.
- There exists a risk of site discontinuation or closure.
- Absence of client-side security and isolation.
The Darknet Browser Panorama: A Comparative Analysis
| Browser | Foundation | Dark Web Mechanism | Open Source | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tor Browser | Firefox | Onion Routing | Yes | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| I2P | Custom | Garlic Routing | Yes | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Brave | Chromium | Tor Integration | Partial | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Opera | Chromium | VPN | No | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Epic | Chromium | Proxy | No | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| GNU IceCat | Firefox | Add-ons | Yes | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| Comodo Dragon | Chromium | Add-ons | No | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| SRWare Iron | Chromium | Add-ons | Mostly | ⭐⭐ |
| Waterfox | Firefox | Add-ons | Yes | ⭐⭐ |
| Darknet Proxy | Custom | Tor | No | ⭐⭐ |
Darknet Browser FAQs
Accessing the dark web is not illegal in and of itself. On the other hand, it is illegal to use the dark web for criminal purposes or to obtain illegal content. It’s critical to recognize that darknet browsers like Tor provide reliable options for maintaining anonymity.
By hiding IP addresses and sending traffic through encrypted tunnels, darknet browsers like Tor offer a high level of anonymity. However, complete anonymity is still unattainable. The desire of intelligence services to de-anonymize Tor users highlights the necessity of taking strict security measures.
Layered encryption and IP masking via onion or garlic routing make it extremely difficult to link dark web activities to specific users. However, situations including firewalls, malware, of incorrect setups, or user error provides a risk of identity disclosure. Advanced international foes might also compromise anonymity.
Yes, darknet browsers like Tor facilitate access to regular internet sites. Nevertheless, due to IP masking, users may appear to connect from a different location, potentially leading to some sites attempting to block Tor users, limiting access.
The NSA and other international espionage organizations cannot completely avoid the darknet. However, with the adoption of strict safety measures, practical anonymity can be attained. Instead of being targeted by sophisticated opponents, Tor and other darknets protect users from widespread surveillance.
The inherent risks of using the dark web include being exposed to viruses, identity theft, scams, and contact with unlawful or immoral content. Users need to be cautious about the websites they visit and the files they download. Furthermore, deanonymization may be possible as a result of browser flaws.
Conclusion
Darknet browsers provide access to the dark web and allow for anonymous browsing. These browsers allow underrepresented groups to enjoy their right to free expression, but they also carry the risk of cybercrime. Therefore, it is crucial to carefully balance the benefits and drawbacks before engaging in dark web activity. Utilize strong anonymity mechanisms and take into account the ethical and legal repercussions to reduce risks.
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, please note that the information provided on this page is not intended to be and should not be interpreted as legal, tax, investment, financial, or any other form of advice. It is important to only invest what you can afford to lose and to seek independent financial advice if you have any doubts. For further information, we suggest referring to the terms and conditions as well as the help and support pages provided by the issuer or advertiser. MetaversePost is committed to accurate, unbiased reporting, but market conditions are subject to change without notice.
About The Author
Damir is the team leader, product manager, and editor at Metaverse Post, covering topics such as AI/ML, AGI, LLMs, Metaverse, and Web3-related fields. His articles attract a massive audience of over a million users every month. He appears to be an expert with 10 years of experience in SEO and digital marketing. Damir has been mentioned in Mashable, Wired, Cointelegraph, The New Yorker, Inside.com, Entrepreneur, BeInCrypto, and other publications. He travels between the UAE, Turkey, Russia, and the CIS as a digital nomad. Damir earned a bachelor's degree in physics, which he believes has given him the critical thinking skills needed to be successful in the ever-changing landscape of the internet.
More articles

Damir is the team leader, product manager, and editor at Metaverse Post, covering topics such as AI/ML, AGI, LLMs, Metaverse, and Web3-related fields. His articles attract a massive audience of over a million users every month. He appears to be an expert with 10 years of experience in SEO and digital marketing. Damir has been mentioned in Mashable, Wired, Cointelegraph, The New Yorker, Inside.com, Entrepreneur, BeInCrypto, and other publications. He travels between the UAE, Turkey, Russia, and the CIS as a digital nomad. Damir earned a bachelor's degree in physics, which he believes has given him the critical thinking skills needed to be successful in the ever-changing landscape of the internet.


















































