Hiroshima AI Process


What is Hiroshima AI Process?
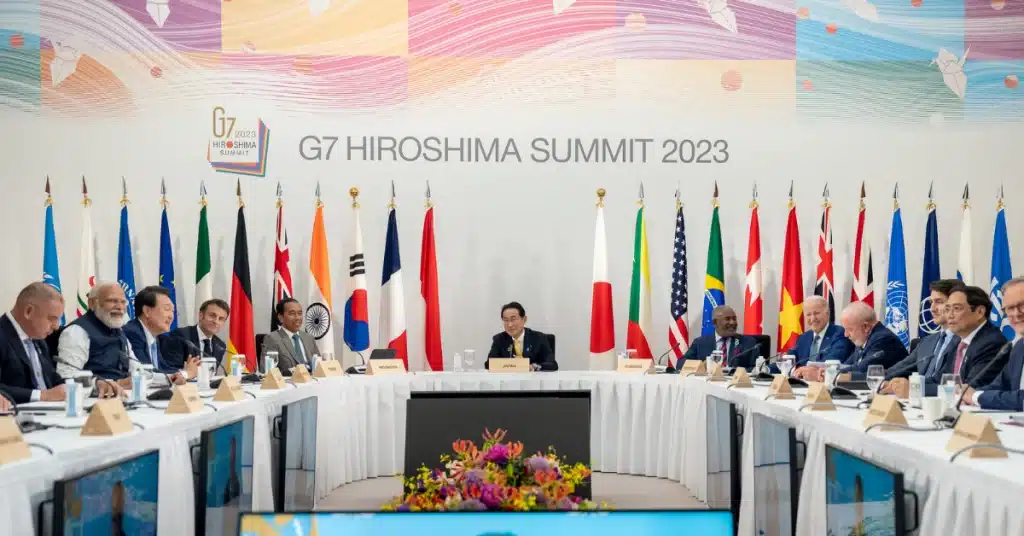
This year, Japan hosted the G7 summit in May 2023, as it does every year. The European Union, Canada, Japan, Italy, France, the United States, and the United Kingdom are among the nations represented in the G7 Summit. The location was Hiroshima and AI was the main topic of discussion at this G7 conference. The most important conclusions from this summit show that leaders prioritized strengthening the regulatory framework to reduce the possible hazards associated with AI and accelerating the use of AI for advantageous use cases in the government and economy.
Understanding of Hiroshima AI Process
In May 2023, G7 countries agreed to prioritise collaboration for inclusive AI governance, seeking to develop secure and reliable systems while maximising the benefits of the technology, including for developing and emerging economies, by bridging digital divides.
The Hiroshima principles for advanced AI models, including foundational models and generative AI systems were endorsed by the G7 last October. They are a set of 11 international guiding principles intended to apply to all AI actors and cover the design, development, deployment and use of advanced AI systems.
- Take appropriate measures throughout the development of advanced AI systems including prior to and throughout their deployment and placement on the market, to identify, evaluate, and mitigate risks across the AI lifecycle.
- Identify and mitigate vulnerabilities, and, where appropriate, incidents and patterns of misuse, after deployment including placement on the market.
- Publicly report advanced AI systems’ capabilities, limitations and domains of appropriate and inappropriate use, to support ensuring sufficient transparency, thereby contributing to increase accountability.
- Work towards responsible information sharing and reporting of incidents among organizations developing advanced AI systems including with industry,governments, civil society, and academia.
- Develop, implement and disclose AI governance and risk management policies, grounded in a risk-based approach – including privacy policies, and mitigation measures, in particular for organizations developing advanced AI systems.
- Invest in and implement robust security controls, including physical security, cybersecurity and insider threat safeguards across the AI lifecycle.
- Develop and deploy reliable content authentication and provenance mechanisms, where technically feasible, such as watermarking or other techniques to enable users to identify AI-generated content.
- Prioritize research to mitigate societal, safety and security risks and prioritize investment in effective mitigation measures.
- Prioritize the development of advanced AI systems to address the world’s greatest challenges, notably but not limited to the climate crisis, global health and education.
- Advance the development of and, where appropriate, adoption of international technical standards.
- Implement appropriate data input measures and protections for personal data and intellectual property.
These principles have in turn served as the basis for the creation of a code of conduct for AI developers. Adherence by companies to these principles is voluntary and would logically have to be adapted to the specificities of each jurisdiction.
Latest News about Hiroshima AI Process
- The G7 industrial countries are set to agree on a code of conduct for companies developing advanced artificial intelligence systems. The 11-point code aims to promote safe, secure, and trustworthy AI globally. The process, initiated during the “Hiroshima AI process,” aims to address privacy concerns and security risks. The code mandates companies to publicly disclose reports on AI capabilities, limitations, and misuse.
- UK Prime Minister Rishi Sunak has announced the world’s first AI Safety Institute, aiming to evaluate and test AI models to address bias, misinformation, and extreme threats. The summit, scheduled for November 1-2, will bring together AI stakeholders and experts to establish an international consensus on AI safety. The UK’s cautious stance on AI regulation and its focus on innovation will be highlighted.
Latest Social Posts about Hiroshima AI Process
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, please note that the information provided on this page is not intended to be and should not be interpreted as legal, tax, investment, financial, or any other form of advice. It is important to only invest what you can afford to lose and to seek independent financial advice if you have any doubts. For further information, we suggest referring to the terms and conditions as well as the help and support pages provided by the issuer or advertiser. MetaversePost is committed to accurate, unbiased reporting, but market conditions are subject to change without notice.
About The Author
Viktoriia is a writer on a variety of technology topics including Web3.0, AI and cryptocurrencies. Her extensive experience allows her to write insightful articles for the wider audience.
More articles

Viktoriia is a writer on a variety of technology topics including Web3.0, AI and cryptocurrencies. Her extensive experience allows her to write insightful articles for the wider audience.