From San Francisco’s Innovation Hub to Tokyo’s Job Surge: How the World’s Metropolises Are Pioneering AI Growth


In Brief
Avantis AI’s study on AI readiness in major urban centers reveals complex factors influencing technological prowess, including job advertising, AI events, AI enterprises, AI Readiness Index, and public interest.

A recent study by Avantis AI has shed light on the AI readiness of major urban centers, revealing a complex interplay of factors that contribute to a city’s technological prowess. This report offers insightful information on the tactics used by various metropolises in their quest to draw in talent, encourage creativity, and position themselves as leaders in the AI future.
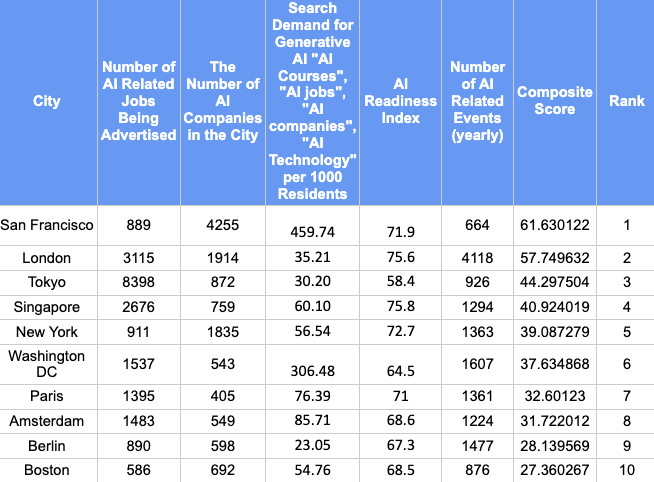
The research analyzed 21 locations globally, focusing on five main indicators: AI-related job advertising, AI events, the existence of AI enterprises, an AI Readiness Index, and public interest in AI-related phrases. By looking at these variables, scientists want to paint a complete picture of the AI ecosystem in each city as well as its prospects for future expansion and advancement in this important area.
The Global Race for AI Supremacy: Cities Vying for Technological Dominance
At the forefront of this technological race stands San Francisco, which secured the top position in the rankings with a composite score of 61.63. The city’s dominance is largely attributed to its impressive count of 4,255 AI companies, the highest among all analyzed urban centers. This concentration of AI-focused businesses creates a fertile ground for innovation, collaboration, and the exchange of ideas. San Francisco’s high AI readiness score of 71.9 further underscores its commitment to embracing and advancing AI technologies.
However, San Francisco’s leadership position is not without challenges. Despite its high number of AI companies, the city advertises only 889 AI-related jobs, significantly fewer than some of its competitors. This discrepancy raises questions about the nature of San Francisco’s AI ecosystem. Are the existing companies primarily focused on research and development rather than large-scale employment? Or is there a mismatch between the skills demanded by these companies and the available talent pool?
London emerges as a strong contender in the global AI race, securing the second position with a composite score of 57.75. The British capital distinguishes itself by hosting an impressive 4,118 AI-related events annually, the highest number among all cities studied. This vibrant event scene suggests a strong emphasis on knowledge sharing, networking, and community building within London’s AI sector. With 1,914 AI companies and an AI readiness index of 75.6, London demonstrates a balanced approach to fostering its AI ecosystem.
The contrast between London and San Francisco in terms of events and job advertisements is striking. While London hosts significantly more AI-related events, it advertises 3,115 AI-related jobs compared to San Francisco’s 889. This disparity might indicate different strategies for growth and development in the AI sector. London appears to be focusing on creating a dynamic, interconnected community of AI professionals and enthusiasts, while San Francisco’s approach seems more centered on nurturing a concentrated cluster of highly specialized AI firms.
What About Asia?
Tokyo’s third-place ranking, with a composite score of 44.30, offers yet another perspective on AI development strategies. The Japanese capital stands out with an astounding 8,398 AI-related job advertisements, far surpassing all other cities in the study. This figure suggests a robust demand for AI talent and a strong push towards integrating AI across various sectors of Tokyo’s economy. However, with only 872 AI companies, Tokyo’s approach seems to be driven more by established industries adopting AI rather than a proliferation of AI-specific startups.
The disparity between Tokyo’s job market and its number of AI companies raises intriguing questions about the nature of AI adoption in different cultural and economic contexts. Are Tokyo’s traditional industries more aggressively integrating AI into their operations, creating a surge in demand for skilled professionals? Or is the city actively working to position itself as a global center for AI talent, potentially attracting professionals from around the world?
Singapore’s fourth-place ranking, with a composite score of 40.92, highlights the city-state’s strategic approach to AI development. Boasting the highest AI readiness index of 75.8, Singapore demonstrates a strong governmental and institutional commitment to fostering AI growth. This high readiness score, combined with a search demand of 60.10 for AI terms per 1,000 residents, suggests a well-coordinated effort to not only develop AI capabilities but also to engage the public in this technological shift.
The success of Singapore in this ranking underscores the importance of government support and public engagement in building a thriving AI ecosystem. By creating an environment that is conducive to AI development and actively promoting public interest in AI technologies, Singapore has positioned itself as a key player in the global AI landscape, particularly within Asia.
New York’s fifth-place position, with a composite score of 39.09, reflects the city’s balanced approach to AI development. With 1,835 AI companies and a high AI readiness index of 72.7, New York demonstrates a solid foundation for AI innovation. The city’s relatively high search demand for AI terms (56.54 per 1,000 residents) indicates significant public interest in AI technologies. However, with only 911 AI-related jobs advertised, New York faces a similar challenge to San Francisco in translating its robust AI company presence into widespread job creation.
The rankings of cities like Washington D.C., Paris, Amsterdam, Berlin, and Boston in the lower half of the top ten provide valuable insights into the diverse approaches to AI development across different urban centers. Washington D.C., for instance, stands out with its exceptionally high public interest in AI, boasting a search demand of 306.48 per 1,000 residents. This figure, second only to San Francisco, suggests a population that is highly engaged with AI concepts and developments.
Paris and Amsterdam’s positions in the rankings highlight the growing importance of European cities in the global AI landscape. With solid AI readiness indices and a growing number of AI companies, these cities are working to establish themselves as key players in the AI revolution. Their efforts demonstrate the increasing recognition of AI’s importance across different regions and cultures.
Berlin’s position in the rankings offers an interesting case study of the challenges of building public engagement with AI technologies. Despite having a respectable number of AI companies and hosting numerous AI-related events, Berlin shows the lowest public interest in AI terms among the top ten cities. This disconnect between the city’s AI infrastructure and public engagement raises questions about the factors that drive popular interest in emerging technologies.
Boston’s ranking rounds out the top ten, showcasing a well-established but smaller-scale AI community compared to its peers. With a solid number of AI companies and a high AI readiness index, Boston demonstrates the potential for smaller urban centers to carve out significant roles in the global AI ecosystem.
All the Factors Matter
The study’s varied approaches and findings demonstrate how difficult it is to create a robust AI ecosystem. Cities are engaged in a complex contest that includes public participation, talent recruiting, economic growth, and government assistance rather than just a single front.
Different political agendas, cultural perspectives on technology, and economic systems are reflected in the disparities in approach across these cities. Certain cities, such as San Francisco, have become leaders in AI innovation by utilizing their pre-existing digital infrastructure. Others, like Tokyo, are growing their AI workforce at a quick pace, which might lead to the integration of AI technology and the transformation of existing sectors.
Cities like London amply highlight the relevance of events and community building in supporting AI growth. These cities are fostering the human connections that propel innovation and advancement in the field of artificial intelligence by establishing venues for networking and information sharing.
The success of cities like as Singapore serves as proof that the significance of public involvement and government assistance cannot be overemphasized. AI development and adoption are facilitated by a favorable regulatory framework and a knowledgeable, engaged public.
This study’s rankings give an overview of the state of AI today, but things are changing.
The worldwide battle to become the AI superpower is not only between cities; rather, it is a group endeavor to use AI to its fullest capacity in order to improve urban living. These cities are paving the way for a future in which artificial intelligence is seamlessly woven into the fabric of urban existence, advancing progress and raising living standards for people everywhere. They are doing this by continuously innovating and evolving their approaches to AI development.
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, please note that the information provided on this page is not intended to be and should not be interpreted as legal, tax, investment, financial, or any other form of advice. It is important to only invest what you can afford to lose and to seek independent financial advice if you have any doubts. For further information, we suggest referring to the terms and conditions as well as the help and support pages provided by the issuer or advertiser. MetaversePost is committed to accurate, unbiased reporting, but market conditions are subject to change without notice.
About The Author
Victoria is a writer on a variety of technology topics including Web3.0, AI and cryptocurrencies. Her extensive experience allows her to write insightful articles for the wider audience.
More articles

Victoria is a writer on a variety of technology topics including Web3.0, AI and cryptocurrencies. Her extensive experience allows her to write insightful articles for the wider audience.


















































