Inside the Global Efforts to Dismantle North Korea’s Cryptocurrency-Fueled Weapons Program


In Brief
South Korea sanctioned 15 North Korean IT workers and a company for funding Pyongyang’s nuclear weapons program.

In a clear move to counter North Korea’s illegal operations, South Korea sanctioned 15 North Korean IT workers and one company for allegedly supplying funding for Pyongyang’s nuclear weapons program. This action emphasizes the necessity for collective vigilance against state-backed cyber activities and the growing international attention being paid to the confluence of cybercrime and global security.
The Scope of the Sanctions
New unilateral sanctions against individuals and groups who raise money for North Korea’s military projects were announced by South Korea’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs on December 26. With effect from December 30, these sanctions expressly target the responsibilities that IT workers and businesses play in funding Pyongyang’s nuclear aspirations.
Members of North Korea’s Munitions Industry Department are specifically targeted by the sanctions, especially the 313 General Bureau, which is in charge of managing the sending of IT personnel outside. Under false pretenses, these workers operate in China, Russia, Southeast Asia, and Africa, among other countries. Their main objective is to earn money by working remotely, with the funds that they make going toward military software projects and the development of nuclear weapons.
Key Individuals and Organizations
Among the selected persons are 14 representatives of the 313 General Bureau, the majority of whom are based in China, including Pak Hung Ryong, Yun Jong Sik, and Ri Il Jin. These people are alleged to have committed fraud in order to get profitable contracts with overseas businesses. Kim Chol Min is one prominent individual who is accused of working illegally for American and Canadian businesses and sending large sums of money to Pyongyang.
Additionally sanctioned is the Korea Kumjong Economic Information Technology Exchange Company. This group is charged with sending IT personnel overseas to make money for North Korea’s military projects. One important figure in this network has been identified as Sin Jong Ho, the leader of Dandong.
The Wider Framework of Cybercrime
The penalties are part of larger initiatives to combat North Korea’s reliance on cybercrime as a source of income. The notorious Lazarus Group and other North Korean hacker organizations have been linked to many high-profile crypto thefts. North Korean hackers stole $1.34 billion worth of digital assets in 2024, a 102% rise from the year before, according to a research by blockchain analytics company Chainalysis. throughout 61% of the overall value taken in cryptocurrency-related events throughout the course of the year may be attributed to this.
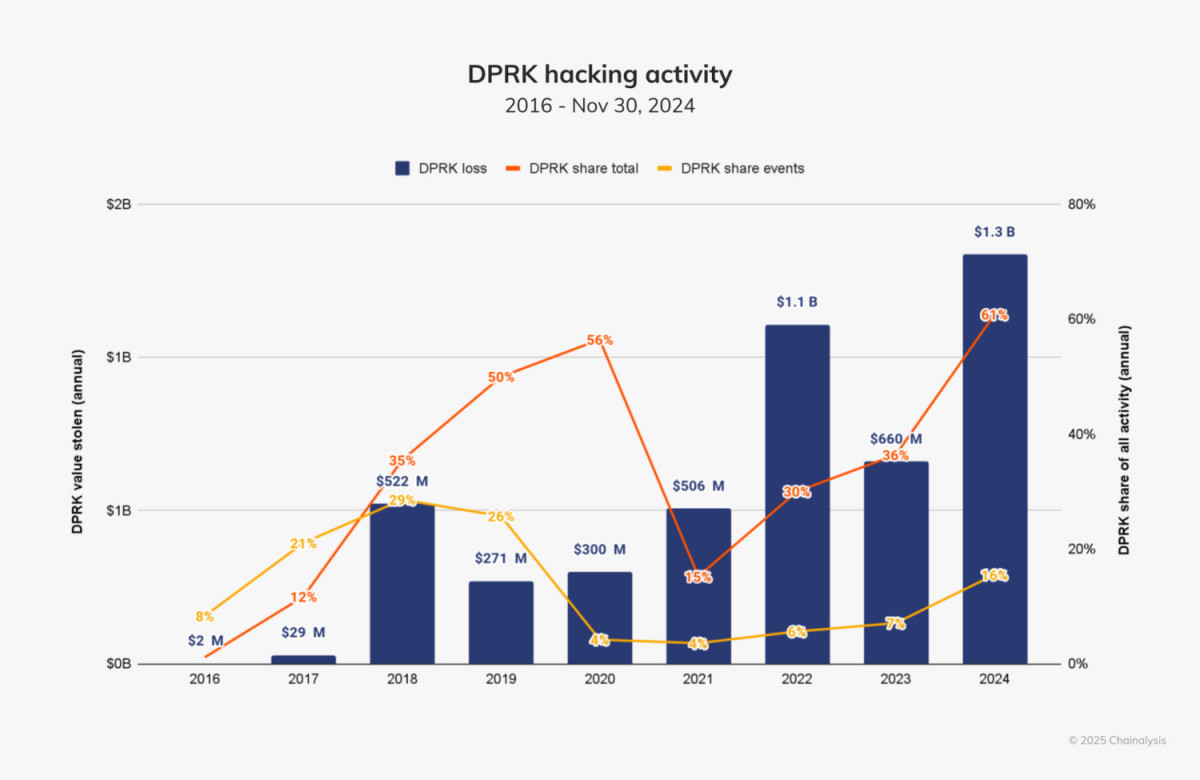
Photo: Chainalysis
These assaults have also become more sophisticated. Recent instances have produced earnings surpassing $100 million, but previous exploits frequently produced profits of less than $50 million. These events highlight North Korean hackers’ increasing skill and boldness.
Cryptocurrency and Unauthorized Funding
Cryptocurrency theft has become a key element of North Korea’s illegal funding scheme. To avoid detection, the stolen money is laundered through intricate networks, frequently involving Chinese bank accounts. The proceeds are then funneled into programs that bolster North Korea’s nuclear and missile capabilities.
The use of cryptocurrencies to finance North Korea’s military initiatives has garnered a lot of interest from across the world. North Korea was held accountable for more over half of the world’s crypto thefts in 2024. The regime’s growing reliance on digital assets to get around sanctions and continue developing weapons is reflected in this trend.
Photo: Chainalysis
The restrictions imposed by South Korea are consistent with those imposed by other countries, such as the US. Kim Ryu Song and 13 other people were indicted by the U.S. Justice Department earlier in December for their roles in a conspiracy that made $88 million over six years. These charges demonstrate how international partners have worked together to confront the problems caused by North Korea’s illegal actions.
Additionally, the UN has stressed how critical it is to address North Korea’s cyber efforts. According to estimates from the U.N. Panel of Experts, up to 40% of North Korea’s revenue for nuclear development is due to cybercrime. This statistic emphasizes how crucial concerted international action is to limiting the regime’s financial resource access.
Consequences for International Security
The financing of nuclear projects through cybercrime poses a serious risk to international security. In addition to disrupting the global financial system, North Korea’s actions increase the dangers of nuclear proliferation. The international community has a special challenge because of the regime’s capacity to make use of advanced technologies and circumvent established sanctions procedures.
The sanctions imposed by South Korea and other countries deter North Korea’s cybercrime. However, dealing with the underlying causes of these problems calls for a diversified strategy. Strengthening cybersecurity measures, improving international collaboration, and closing regulatory gaps in the crypto industry are imperative to reducing the threats presented by state-sponsored cybercrime.
The international community has to be on guard as North Korea is improving its cyber capabilities. The growing complexity of North Korean cyberattacks raises the possibility that conventional enforcement strategies may not be adequate. To combat this changing danger, a proactive strategy that makes use of technology breakthroughs and encourages international cooperation is required.
Efforts to stop North Korea’s illegal actions are probably going to get more intense in 2025 and beyond. Protecting global peace and security will depend heavily on the creation of new instruments and tactics to monitor and stop cybercrime. At the same time, maintaining long-term stability will require tackling the larger geopolitical issues that motivate North Korea’s dependence on cyber activities.
The restrictions imposed by South Korea on North Korean IT personnel and institutions demonstrate the increasing awareness of the part cybercrime plays in financing illegal activity. These actions are a crucial first step in halting North Korea’s nuclear aspirations, especially when combined with global initiatives to address the problems caused by state-sponsored hacking. In order to ensure a safe and stable future as the world continues to change, concerted effort and creative solutions will be crucial.
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, please note that the information provided on this page is not intended to be and should not be interpreted as legal, tax, investment, financial, or any other form of advice. It is important to only invest what you can afford to lose and to seek independent financial advice if you have any doubts. For further information, we suggest referring to the terms and conditions as well as the help and support pages provided by the issuer or advertiser. MetaversePost is committed to accurate, unbiased reporting, but market conditions are subject to change without notice.
About The Author
Victoria is a writer on a variety of technology topics including Web3.0, AI and cryptocurrencies. Her extensive experience allows her to write insightful articles for the wider audience.
More articles

Victoria is a writer on a variety of technology topics including Web3.0, AI and cryptocurrencies. Her extensive experience allows her to write insightful articles for the wider audience.


















































