Blockchain Interoperability: Next Web3 Paradigm Shift


In Brief
This article explores cross-chain architecture and its distinction from multi-chain and highlights interoperability infrastructure providers paving the way for an interconnected blockchain future.
Ethereum’s limited throughput and rising competition for block space have given rise to the appearance of hundreds of separate networks with their unique features: primary layers (L1s), secondary layers (L2s), and specialized application-specific chains (Appchains).
Traditionally, protocols seeking to expand their presence in multiple ecosystems had to fragment their community with multiple instances of the application for each network. However, the landscape is evolving. With the creation of special interoperability infrastructure, the space is shifting towards a more interconnected and inclusive environment.
In this article, let’s discuss the idea behind cross-chain architecture, how it is different from multi-chain, and go through some examples of interoperability infrastructure providers paving the way for an interconnected blockchain future.
What is Multi-chain?
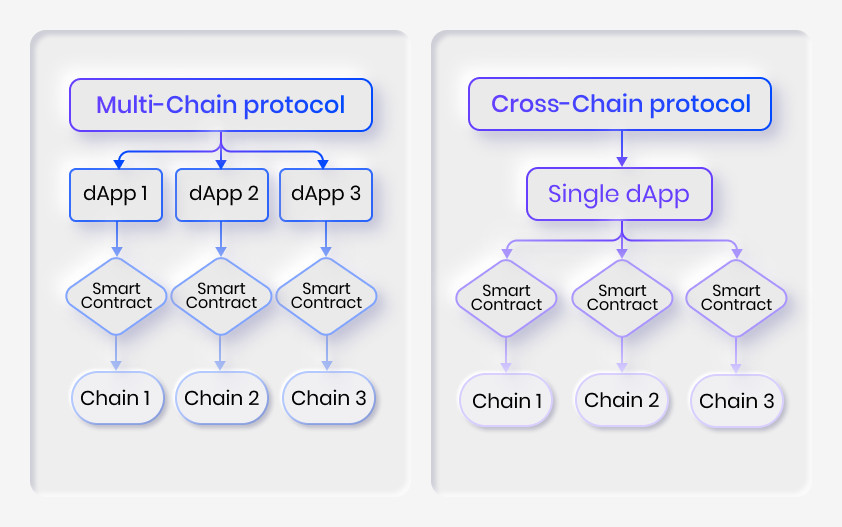
This term refers to protocols and dApps that are launched on multiple blockchains. Developers create and deploy smart contracts for every network and launch a separate instance of their application dedicated to each network.
This means all the dApp instances are effectively isolated, having to manage each their own state leading to capital inefficiency and a barrier for users who might wish to explore opportunities of other blockchains and their ecosystems.
However, there are advantages to this approach as well because extra interoperability layers introduce additional security concerns. Relying on cross-chain bridges for communication and token transfers between networks raises the possibility for vulnerabilities to be found. In an isolated environment, the hack of any one instance of the application will leave operation on other networks unhinged (apart from protocol reputation).
How is it different from Cross-chain?
Integrating a layer of network interoperability into their products allows developers to build unified ecosystems, connecting their users and leveraging unique features of multiple blockchains in one application (e.g., security from chain 1, Low-cost and low-latency token transfers from chain 2, and decentralized storage of metadata on chain 3).
In a cross-chain architecture, smart contracts deployed on different networks are meant to perform separate tasks inside a single product upheld in a single state. Cross-chain bridges allow for the seamless flow of assets and data unifying previously separated environments.
Multi-chain vs. Cross-chain
The key difference between the two designs is the ability to natively transfer tokens and data between networks within one application.
Each approach is characterized by its own set of advantages and is used depending on the distinct use case the developers wish to realize.
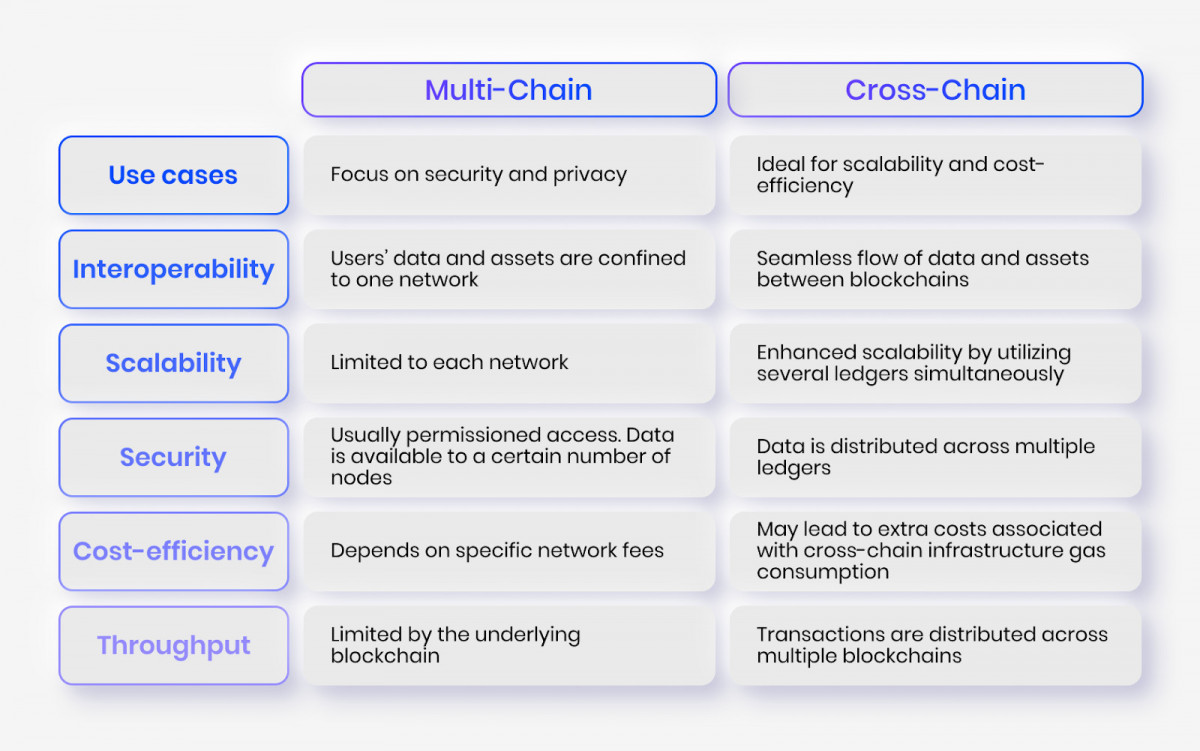
A Multi-chain architecture helps with prioritizing the security and privacy of personal data on multiple networks all within a single ecosystem.
On the other hand, cross-chain protocols focus on interoperability between networks. Efficient distribution of data and transactions between multiple ledgers allows for superior scalability, cost-efficiency, and throughput.
The Solution to Blockchain Interoperability Security
As the advantages that a cross-chain architecture can provide to the space are visible, multiple protocols set themselves with the task of developing the interoperability infrastructure required to usher in the era of securely interconnected blockchains.
Chainlink CCIP
Released in 2023, Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) is a decentralized messaging protocol for the seamless transfer of data and tokens across networks.
It works by routing each cross-chain transaction through multiple independent networks, ensuring the validity and authenticity of each message with both on-chain and off-chain components. Combined with a separate Risk Management Network constantly on the lookout for any discrepancies or potential attacks, the system automatically halts any suspicious transactions.
With CCIP launched on 10 mainnet networks, Chainlink positions itself as the solution to security risks of cross-chain operations and aims to provide protocols built on top with a safe interoperability layer.
Wormhole
Launched in 2021 as a token bridge, it took on a more generalized approach to cross-chain messaging and released Wormhole V2, an interoperability layer for protocols to build upon.
The network is primarily secured by off-chain Guardian nodes running. When the Guardians reach a consensus on the validity of the transaction, it passes to Relayers, who are unable to modify the message. On top of the validity layer, Wormhole employs 2 additional security layers to track suspicious transactions, supply limits, and halt the network in case of violations.
Wormhole has built a robust ecosystem of 200+ connected dApps over 28 blockchains. Even though the set of Guardians is currently limited to 19 nodes, plans are in place to expand their numbers as well as incorporate zk-proof technology to boost security.
LayerZero
Positioned by its developers as an omnichain interoperability protocol, it works as an immutable and trustless lightweight messaging platform across 75+ blockchains.
It provides a unique approach to interoperability allowing users to choose their own set of Decentralized Verifier Networks (DVNs) that will verify their messages. With its recently launched LayerZero V2, message validation is now a 2-step process: Verification by your Security Stack’s DVNs and performing transactions by Executors. In addition, the Pre-crime feature offers an extra layer of security by intercepting malicious transactions before their delivery.
However, the downside of this configurable approach is that protocols using LayerZero need to study the DVNs they wish to use to minimize potential attacks.
The Blockchain Future is Interconnected!
Each blockchain has a set of unique advantages. Some are purpose-built for underlying asset security, others for lightning-fast transactions, others for decentralized data storage, and so on. But they all are distinct islands in the sea of Web3, posing challenges and hazards for navigating between them.
Reliable interoperability infrastructure provides a way to break the walls between different networks. By leveraging the best characteristics of multiple blockchains simultaneously, protocols and dApps are now shifting towards a more interconnected approach, improving capital efficiency for DeFi users, boosting functionality, enhancing scalability, and reconnecting ecosystems spread across multiple blockchains.
By effectively addressing security concerns associated with cross-blockchain messaging and token transfers, the Web3 space is now able to provide singular applications built for efficiency and UX.
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, please note that the information provided on this page is not intended to be and should not be interpreted as legal, tax, investment, financial, or any other form of advice. It is important to only invest what you can afford to lose and to seek independent financial advice if you have any doubts. For further information, we suggest referring to the terms and conditions as well as the help and support pages provided by the issuer or advertiser. MetaversePost is committed to accurate, unbiased reporting, but market conditions are subject to change without notice.
About The Author
Anthony is a blockchain analyst and writer with an academic background in biochemistry. He works as researcher and content creator in the PowerPool protocol, covering ecosystem updates, new DeFi/dePin/AI products, and analysis of various web3 protocols.
More articles

Anthony is a blockchain analyst and writer with an academic background in biochemistry. He works as researcher and content creator in the PowerPool protocol, covering ecosystem updates, new DeFi/dePin/AI products, and analysis of various web3 protocols.


















































