The Explosive Rise of Crypto Theft in 2024 with North Korea Leading the Charge


In Brief
North Korean hackers stole $2.2 billion worth of cryptocurrency assets in 2024, posing a growing threat to global security and the crypto industry.

The cryptocurrency industry saw a tragic turning point in 2024 when hackers took advantage of flaws to steal digital assets valued at $2.2 billion. Of them, North Korean hackers were the most powerful, accounting for $1.3 billion of the money that was taken. An increasing threat to the crypto business and global security is highlighted by the fact that, according to Chainalysis, the value stolen by North Korea-affiliated entities has increased by 102.88% since 2023.
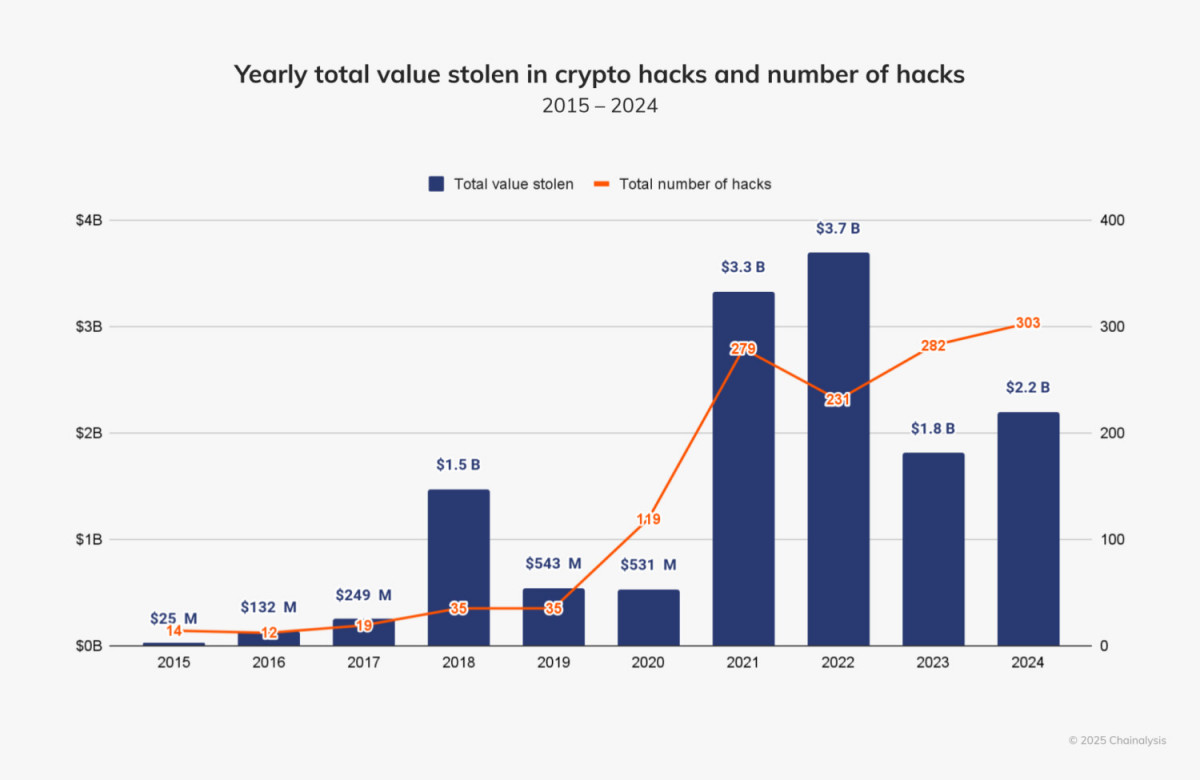
Photo: Chainalysis
The Increasing Trend of Digital Theft
The sector has always struggled with crypto theft, with some years witnessing historically high amounts of money taken. Due to a rise in the frequency and intensity of hacking attacks, the total amount taken in 2024 increased by more than 21% over the previous year. Reports of breaches increased from 282 in 2023 to 303 in total, underscoring the industry’s ongoing vulnerability.
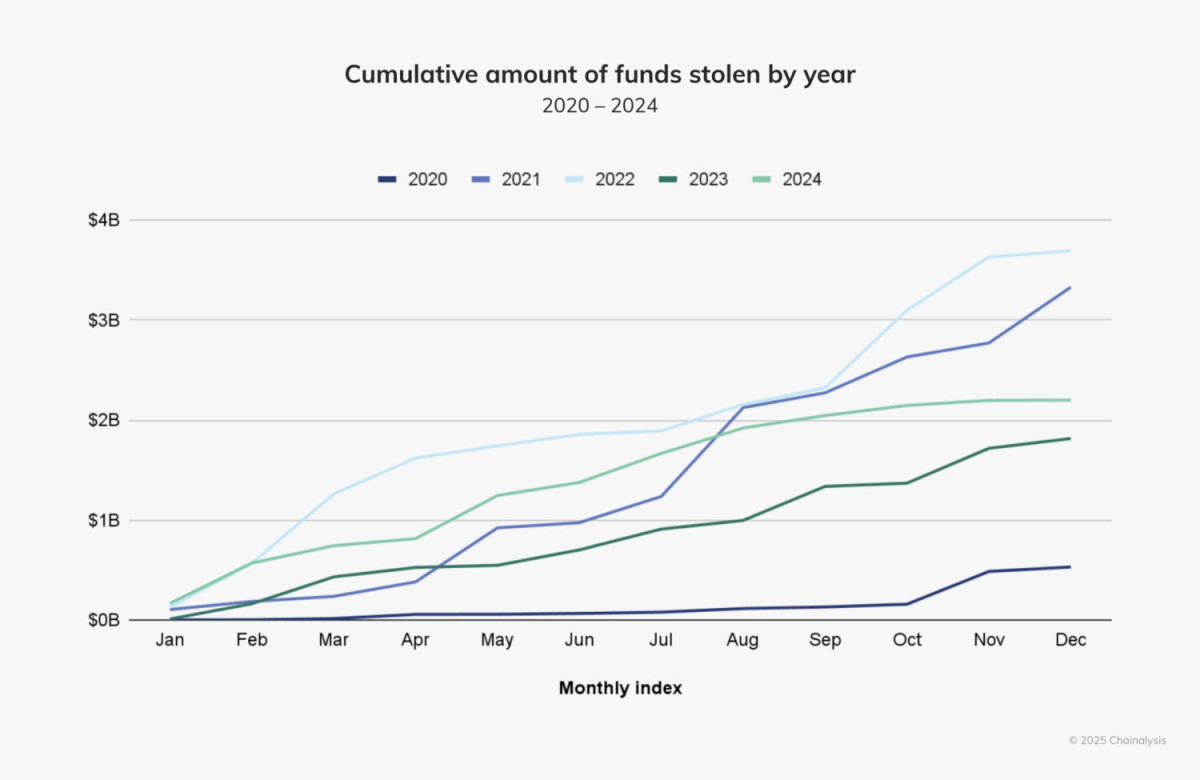
Photo: Chainalysis
In 2024, hacking activities took a different course. Crypto theft totaled $1.58 billion between January and July, an 84.4% rise over the same period in 2023. At first, analysts thought 2024 may be in line with the record-breaking years of 2021 and 2022, when more than $3 billion was stolen every year. However, following the middle of the year, hacking instances substantially decreased, indicating the possibility of outside influences.
Target Shift: Centralized Platforms vs. DeFi
Hackers have historically targeted decentralized finance networks primarily because of their quick development cycles and sometimes inadequate security mechanisms. Most stolen assets in early 2024 were attributed to DeFi. The second and third quarters of the year saw a discernible change, nevertheless, with centralized systems taking the brunt of attacks.
This tendency is seen in two major breaches: the $234.9 million loss from WazirX in July and the $305 million hack of DMM Bitcoin in May. These occurrences highlight centralized services’ weaknesses, especially in relation to private key management. Private key compromises were the most frequent attack vector in 2024, accounting for 43.8% of all crypto thefts.
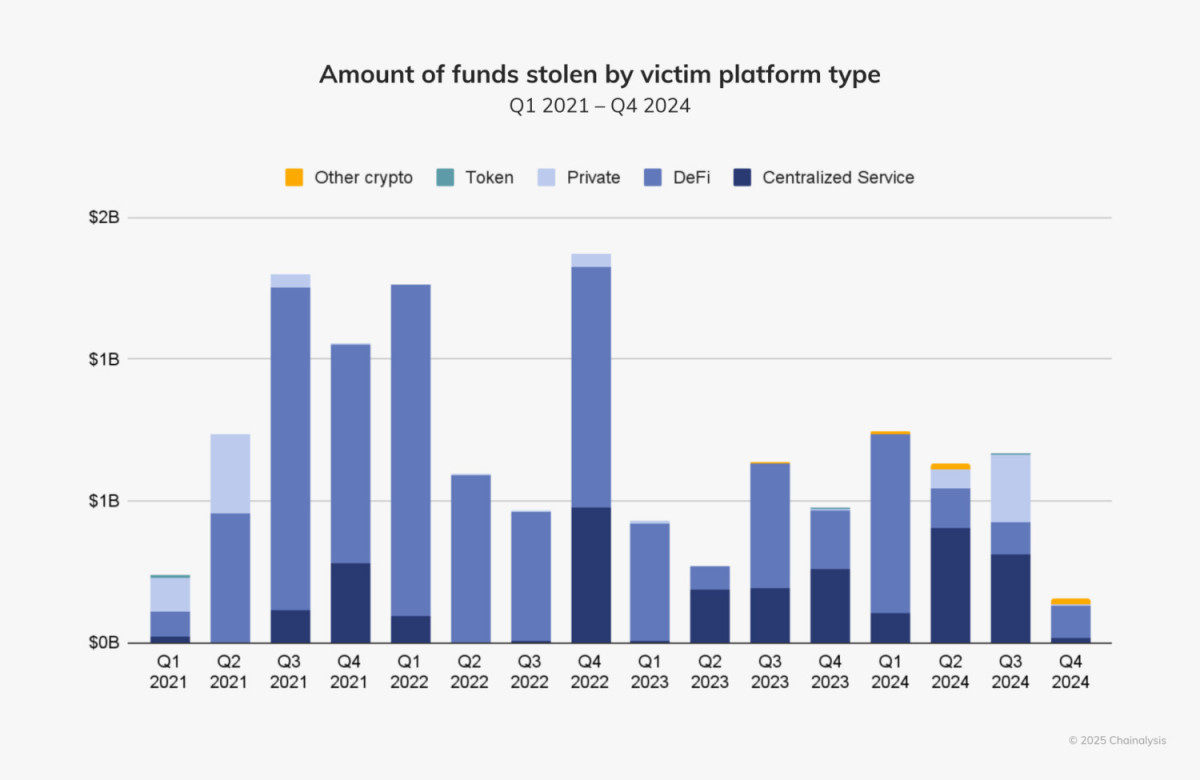
Photo: Chainalysis
An essential part of security are private keys, which provide access to users’ money. The DMM Bitcoin hack shows that any compromise may have disastrous results. In addition to causing financial loss, the exchange’s failure to sufficiently safeguard its private keys ultimately resulted in its shutdown later that year.
A Major Participant in Crypto Hacking – North Korea
The widespread theft of cryptocurrencies has come to be associated with North Korean hackers. They were the most common actors in the space in 2024, accounting for 61% of the total amount taken. The $1.3 billion that was taken in 47 attacks is a substantial increase above the $660.5 million that was taken in 20 hacks in 2023. Pyongyang’s dependence on cryptocurrency theft to finance its weapons programs and get around international sanctions is reflected in this spike in activity.
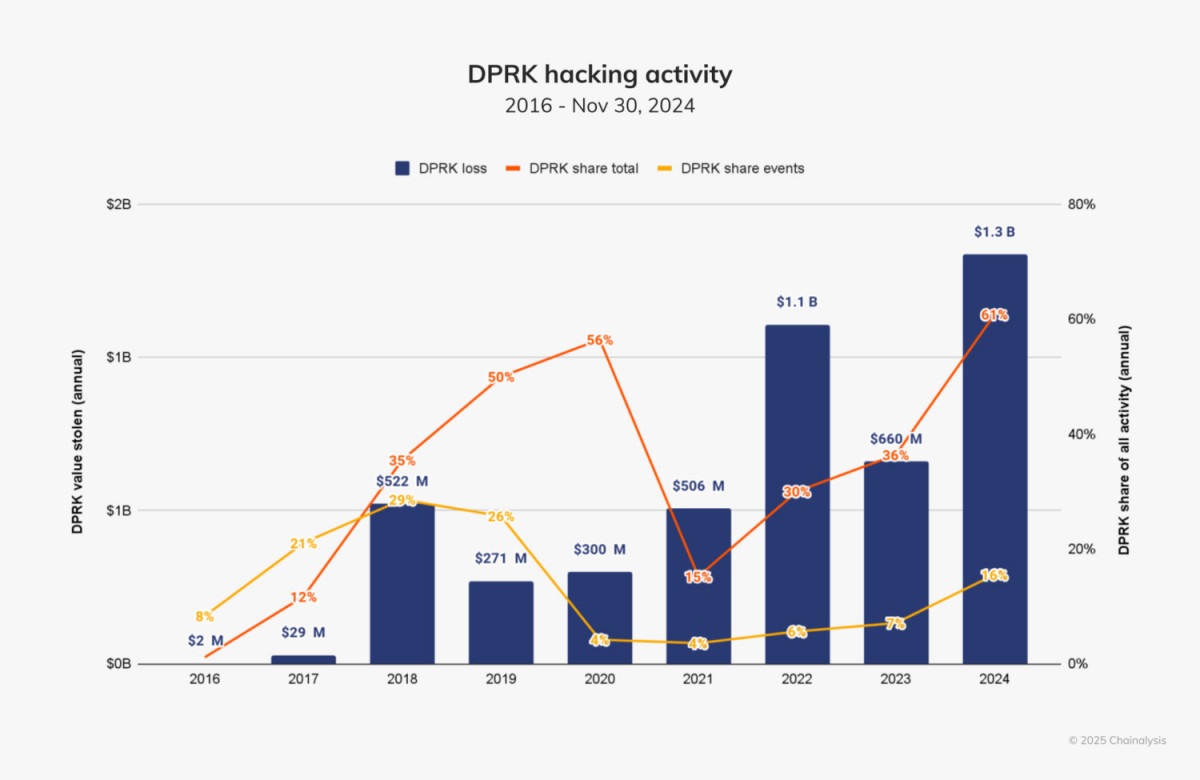
Photo: Chainalysis
North Korean hackers have developed increasingly complex strategies. They carried out large-scale exploits more frequently in 2024, more often aiming for sums over $50 million than in prior years. They also broadened their scope to cover hacks on a lesser scale, aiming for amounts as little as $10,000.
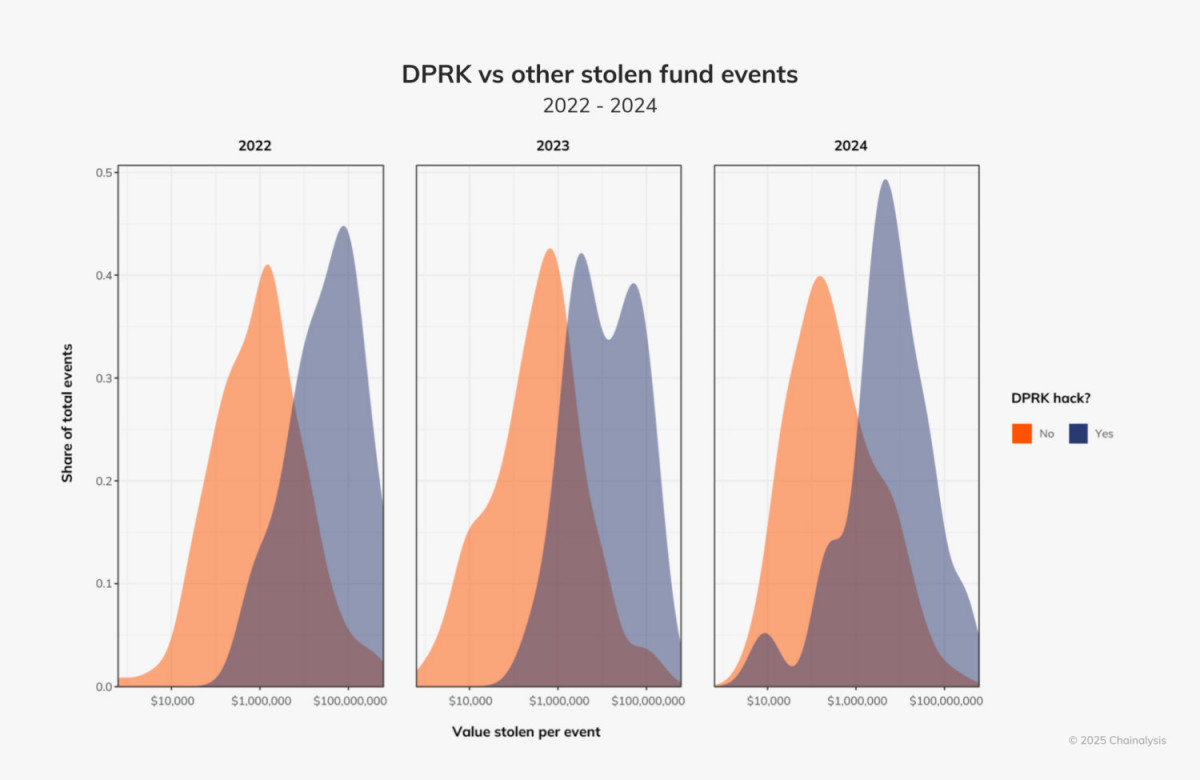
Photo: Chainalysis
Cyber Espionage and Infiltration of the Workforce
The infiltration of crypto firms by North Korean IT professionals is a development concern. To obtain access to critical networks, these agents employ fictitious identities, third-party agents, and distant employment possibilities. In one well-known instance, 14 citizens of North Korea were charged with stealing $88 million using these kinds of techniques. In order to stop such breaches, these strategies emphasize the necessity of rigorous staff screening and strong cybersecurity procedures.
The first half of 2024 saw a sharp increase in North Korean cyber activity, but after July, it significantly decreased. A geopolitical event—a summit between North Korean leader Kim Jong Un and Russian President Vladimir Putin—coincided with this decrease. North Korea’s hacking activities seemed to change after the meeting, as evidenced by a 53.73% decrease in the daily worth of stolen cash. However, within the same time frame, there was a modest rise in hacking activities by non-North Koreans.
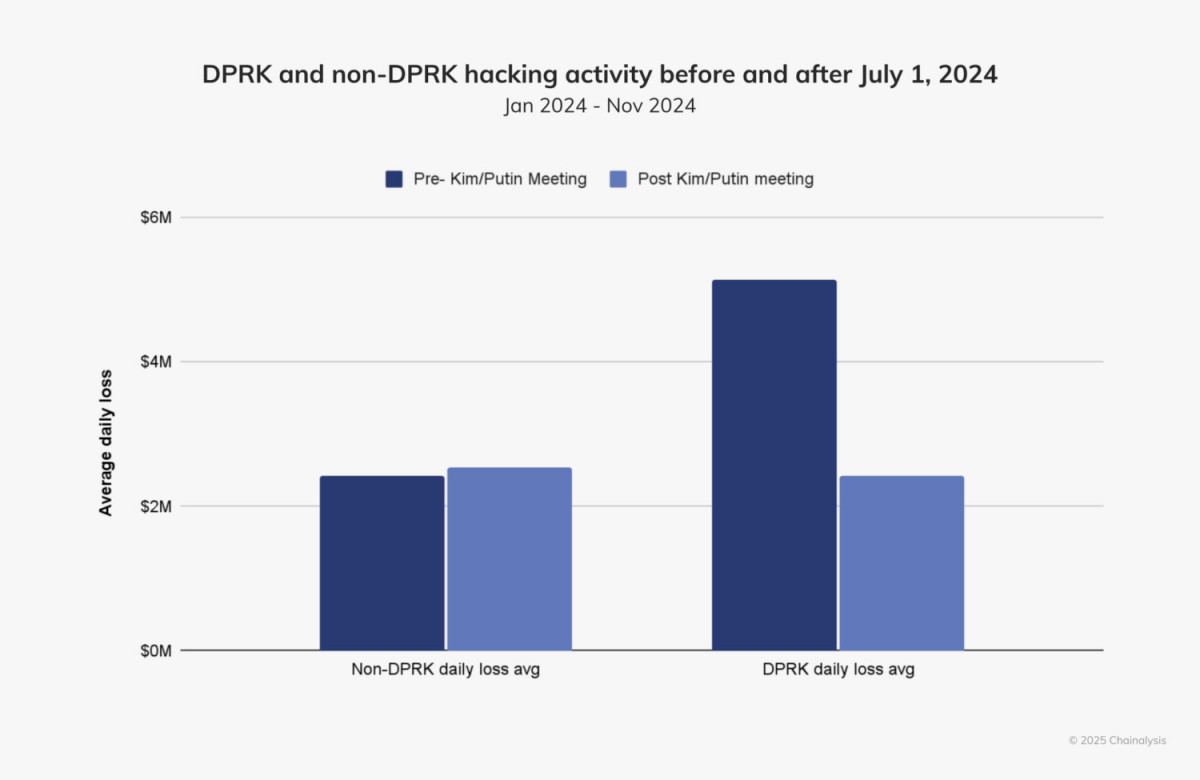
Photo: Chainalysis
The causes of this deterioration are yet unknown. It’s possible that North Korea shifted funds to assist its military partnership with Russia, which has included sending ballistic missiles and people to Ukraine. On the other hand, the delay may be the result of a strategic change in Pyongyang’s cyber activities.
The DMM Bitcoin Breach Case Study
Among the most important events of 2024 was the $305 million DMM Bitcoin breach. North Korean hackers stole 4,502.9 Bitcoin by taking advantage of holes in the exchange’s system that allowed them to get private keys without authorization. After being laundered through mixing services, the stolen money was subsequently moved to platforms connected to the Huione Group, a cybercrime-affiliated company based in Cambodia.
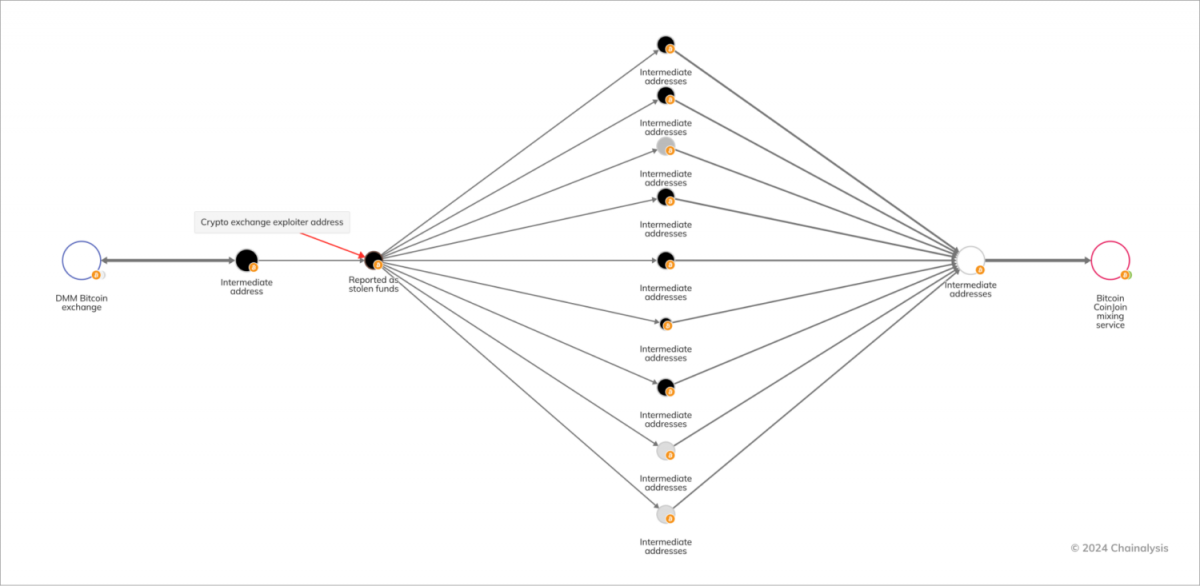
Photo: Chainalysis
This violation has serious repercussions. With the goal of finishing the transformation by 2025, DMM Bitcoin halted operations and transferred its assets to SBI VC Trade. The incident emphasizes the necessity for proactive defenses against such assaults and the disastrous effects of inadequate security measures.
Predictive Models and Crypto Security’s Future
Predictive technology developments give promise in the fight against cryptocurrency theft. The purchase of Web3 security company Hexagate by Chainalysis is a big step in the direction of proactive threat detection. Real-time blockchain activity analysis is done by Hexagate’s machine learning algorithms, which spot questionable trends and possible attacks before they happen.
For instance, two days before the assault, Hexagate discovered a contract connected to a $20 million UwU Lend vulnerability. The early identification shows the potential of such technologies to avert financial losses, even though the link to the ultimate attack was not immediately apparent.
Despite these developments, predictive models’ efficacy hinges on how well they are incorporated into current security systems. To ensure that such dangers are eliminated before they become more serious, protocols must be outfitted with the instruments required to respond to early alerts.
The surge in crypto theft in 2024 emphasizes how urgently improved security measures are needed. Addressing the changing threat landscape requires a cooperative strategy combining regulators, law enforcement, and industry players. A thorough security plan must include solid private key management, sophisticated tracing capabilities, and real-time monitoring.
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, please note that the information provided on this page is not intended to be and should not be interpreted as legal, tax, investment, financial, or any other form of advice. It is important to only invest what you can afford to lose and to seek independent financial advice if you have any doubts. For further information, we suggest referring to the terms and conditions as well as the help and support pages provided by the issuer or advertiser. MetaversePost is committed to accurate, unbiased reporting, but market conditions are subject to change without notice.
About The Author
Victoria is a writer on a variety of technology topics including Web3.0, AI and cryptocurrencies. Her extensive experience allows her to write insightful articles for the wider audience.
More articles

Victoria is a writer on a variety of technology topics including Web3.0, AI and cryptocurrencies. Her extensive experience allows her to write insightful articles for the wider audience.


















































